Free Flu Vaccines for All Patients
We’re now offering free flu vaccines at our clinic — available to all patients with no eligibility restrictions. Please call ahead to confirm vaccine availability, as stock may vary.
We’re now offering free flu vaccines at our clinic — available to all patients with no eligibility restrictions. Please call ahead to confirm vaccine availability, as stock may vary.
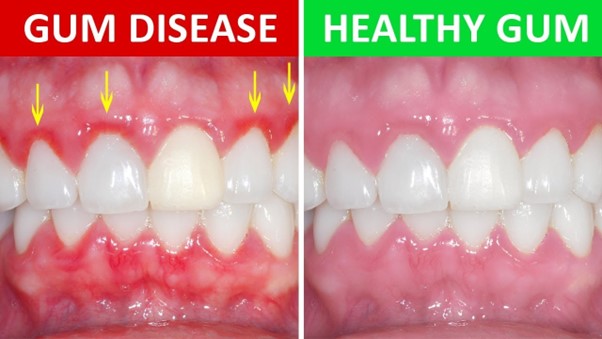
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a bacterial infection that affects your gums. If your gums are swollen or bleed easily, it is possible that you might have gum disease as these are the early signs. Having bad breath, which is usually a result from the blood and lack of oral hygiene, is also another early sign.
The early stage of gum disease is called gingivitis, and if left untreated, it may progress into the later stage called periodontitis. At this stage, your teeth will become rather loose and form gum pockets, which are the spaces between the gums and teeth. Bacteria could easily get stuck in these pockets, resulting in further damage to your dental health. Therefore, it is important to treat gum disease as early as possible.
There are several factors that could cause gum disease, including:
The receding gums and increasing gum pockets caused by gum disease may lead to tooth loss. Additionally, some researchers have suggested that gum disease may also increase the possibilities of serious health issues, including diabetes, lung disease, heart disease, and premature birth.
To avoid the risks and complications of having a gum disease, getting a proper treatment is a wise decision and a good step for better health. There are several treatments available to repair your gums, varying based on the levels of severity that each suit most.
How Do Gum Disease Treatments Work?
Firstly, your dentist will perform a dental exam, checking the gums’ firmness and condition, size and depth of gum pockets, teeth alignment, and jawbones. They will also conduct a dental hygiene evaluation to see if your oral hygiene has been adequate.
Next, your dentist will determine the most suitable treatment depending on the severity of your condition. Here are some of the treatments that can be done:
After the treatment, your dentist will prescribe certain medications that need to be taken to lessen the swelling and discomfort.
You are also only allowed to consume soft food and food that cannot be easily stuck in teeth, avoid hot and cold food and beverages, avoid spicy and acidic food, chew carefully on the side that is not affected by the treatment, and you are not allowed to smoke and consume alcohol for 2-14 days after the treatment. The use of straw is also prohibited as the suction will interfere with the healing process.
Additionally, you will be required to rinse your mouth using salt water 2-3 times daily to reduce the inflammation. If you experience any major discomfort or swelling, contact your dentist immediately.
Moreover, it is important to maintain good oral hygiene after your gum disease has been treated. Remember to brush your teeth twice a day, floss, and use mouthwash regularly to prevent gum disease from happening again.
It depends on the severity of your gum disease. Some may heal in several days, while more serious cases take months to recover.
Gum disease is often painless, so even if you are not experiencing any pain or discomfort, you may have gum disease.
If you are experiencing symptoms of gum disease, or if you are interested in doing a dental check-up, schedule an appointment at Supernova Medical Centre with Dentist now before the condition becomes more serious. Professionals at the clinic will help you uncover details regarding your dental condition and they will assist you in selecting the most suitable treatment for your gum disease.










We are a Bulk Billing clinic for patients with a valid Medicare card.

We also offer Direct Billing through Private Health Insurance, including: Allianz, Bupa, Medibank, NIB, AHM, HICAPS-linked providers
For eligible services, we can process claims on the spot via HICAPS, making your visit seamless and hassle-free.
Please contact our reception team to confirm coverage and eligibility prior to your appointment.




